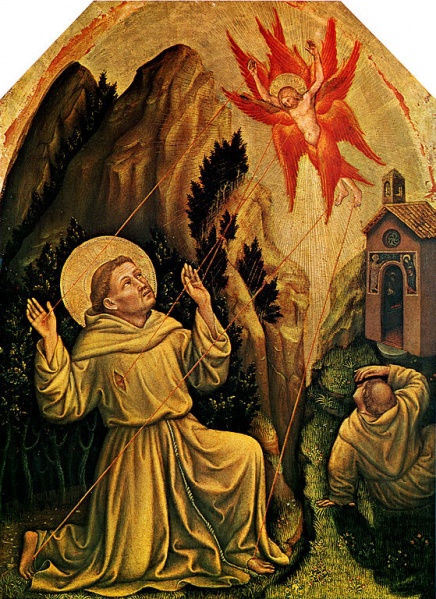
St Francis receives the Stigmata
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7St Thomas Aquinas | 8 |
| 9St Frances of Rome | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17St Patrick of Ireland | 18 | 19St Joseph | 20 | 21St Benedict of Nursia | 22 |
| 23 | 24St Gabriel | 25Feast of the Annunciation | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | |||||
Mystical Stigmata
To decide merely the facts without deciding whether or not they may be explained by supernatural causes, history tells us that many ecstatics bear on hands, feet, side, or brow the marks of the Passion of Christ with corresponding and intense sufferings. These are called visible stigmata. Others only have the sufferings, without any outward marks, and these phenomena are called invisible stigmata.
Their existence is so well established historically that, as a general thing, they are no longer disputed by unbelievers, who now seek only to explain them naturally. Thus a free-thinking physician, Dr. Dumas, professor of religious psychology at the Sorbonne, clearly admits the facts (Revue des Deux Mondes, 1 May, 1907), as does also Dr. Pierre Janet (Bulletin de l’Institut psychologique international, Paris, July, 1901).
St. Catherine of Siena at first had visible stigmata but through humility she asked that they might be made invisible, and her prayer was heard. This was also the case with St. Catherine de’ Ricci, a Florentine Dominican of the sixteenth century, and with several other stigmatics. The sufferings may be considered the essential part of visible stigmata; the substance of this grace consists of pity for Christ, participation in His sufferings, sorrows, and for the same end–the expiation of the sins unceasingly committed in the world. If the sufferings were absent, the wounds would be but an empty symbol, theatrical representation, conducing to pride. If the stigmata really come from God, it would be unworthy of His wisdom to participate in such futility, and to do so by a miracle.
But this trial is far from being the only one which the saints have to endure: “The life of stigmatics,” says Dr. Imbert, “is but a long series of sorrows which arise from the Divine malady of the stigmata and end only in death: (op. cit. infra, II, x). It seems historically certain that ecstatics alone bear the stigmata; moreover, they have visions which correspond to their rôle of co-sufferers, beholding from time to time the blood-stained scenes of the Passion.
With many stigmatics these apparitions were periodical, e.g., St. Catherine de’ Ricci, whose ecstasies of the Passion began when she was twenty (1542), and the Bull of her canonization states that for twelve years they recurred with minute regularity. The ecstasy lasted exactly twenty-eight hours, from Thursday noon till Friday afternoon at four o’clock, the only interruption being for the saint to receive Holy Communion. Catherine conversed aloud, as if enacting a drama. This drama was divided into about seventeen scenes. On coming out of the ecstasy the saint’s limbs were covered with wounds produced by whips, cords etc.
Dr. Imbert has attempted to count the number of stigmatics, with the following results:
The first mentioned is St. Francis of Assisi, in whom the stigmata were of a character never seen subsequently; in the wounds of feet and hands were excrescences of flesh representing nails, those on one side having round back heads, those on the other having rather long points, which bent back and grasped the skin. The saint’s humility could not prevent a great many of his brethren beholding with their own eyes the existence of these wonderful wounds during his lifetime as well as after his death. The fact is attested by a number of contemporary historians, and the feast of the Stigmata of St. Francis is kept on 17 September.
APA citation. (1912). Mystical Stigmata. In The Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved September 18, 2022 from New Advent: http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/14294b.htm